When embarking on electrical projects that require underground installations, selecting the right Direct Burial Wire is crucial not only for the integrity of the wiring but also for ensuring safety and compliance with industry standards. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), the proper choice of wire type can significantly affect the performance and longevity of electrical systems. A recent report from the Electrical Safety Foundation International indicates that improper wiring choices contribute to a notable percentage of electrical failures, emphasizing the importance of adhering to best practices when it comes to using Direct Burial Wire in outdoor applications.
Direct Burial Wire is specifically designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including moisture, extreme temperatures, and soil acidity. Using wires that are not rated for direct burial can lead to insulation breakdown and potential hazards, which can be costly both financially and in terms of safety. The 2021 Electrical Wire and Cable Manufacturing report highlighted that the demand for reliable and durable wiring solutions is on the rise, as more homeowners and contractors prioritize safety and efficiency in electrical installations. Therefore, understanding the specifications, coating materials, and installation guidelines of Direct Burial Wire is essential for successful project outcomes, ensuring both compliance with relevant standards and the protection of valuable equipment.

Direct burial wire is a specialized type of electrical wire designed for underground installation without the need for additional conduit protection. This wire is often insulated with materials that can withstand moisture, temperature fluctuations, and soil chemicals, making it suitable for various applications including landscaping lighting, irrigation systems, and even in commercial settings for underground service connections. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), properly installed direct burial wire can last over 30 years, significantly contributing to the longevity of electrical projects.
Understanding the specifications of direct burial wire is crucial for ensuring safety and functionality. These wires come in various gauges and insulation types, such as UF (Underground Feeder) cable and USE (Underground Service Entrance) wire, each tailored for specific uses. For instance, UF cable, composed of moisture-resistant materials, is ideal for residential landscaping projects, while USE wire is often used for more robust installations. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) recommends selecting wire gauges based on the total amperage of the application, emphasizing the importance of meeting electrical codes to avoid issues such as overheating and electrical failures. By following these guidelines and understanding the properties of direct burial wire, electricians and DIY enthusiasts can make informed decisions for their electrical installations.
This bar chart illustrates the various applications of direct burial wire across different sectors. The data shows the number of applications in thousands for each type, highlighting the significance of direct burial wire in residential, commercial, industrial, irrigation, and telecommunications projects.

When selecting direct burial wire for your electrical projects, several key factors must be carefully evaluated to ensure safety and functionality. Firstly, consider the wire gauge; this determines the amount of current the wire can safely carry. For underground installations, a thicker gauge wire is often necessary to handle the demands of outdoor use and prevent overheating. Additionally, the voltage rating of the wire should align with your project requirements to avoid potential failures or hazards.
Another vital aspect to take into account is the insulation type of the direct burial wire. Wires designed for underground use typically feature robust insulation materials that protect against moisture, soil conditions, and potential physical damage. Look for wires with water-resistant and UV-stable coatings, ensuring they can withstand prolonged exposure to the elements. Lastly, assess the installation depth; local codes may dictate how deep the wire must be buried to avoid interference with other utilities and to comply with safety regulations. By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right direct burial wire that meets your project needs effectively and safely.
When selecting the right direct burial wire for your electrical projects, it is essential to understand the different types available and their unique characteristics. Typically, direct burial wires come in three main varieties: UF (Underground Feeder) cable, sunlight-resistant cables, and THWN (Thermoplastic Heat and Water resistant Nylon-coated) wires. Each type is designed for specific applications and environmental conditions, making it crucial to choose the right one for optimal performance.
UF cable is commonly used for underground installations, as it is moisture-resistant and durable, designed to withstand direct exposure to soil. It typically consists of multiple conductors encased in a solid, waterproof outer jacket.
Sunlight-resistant cables are suitable for applications that may be exposed to UV rays, such as outdoor lighting. These cables incorporate special materials that protect against degradation from sun exposure.
THWN wires are versatile and can be used in both wet and dry locations, offering flexibility in a variety of installations. Understanding these characteristics ensures that your choice aligns with the specific needs of your project, promoting safety and longevity.
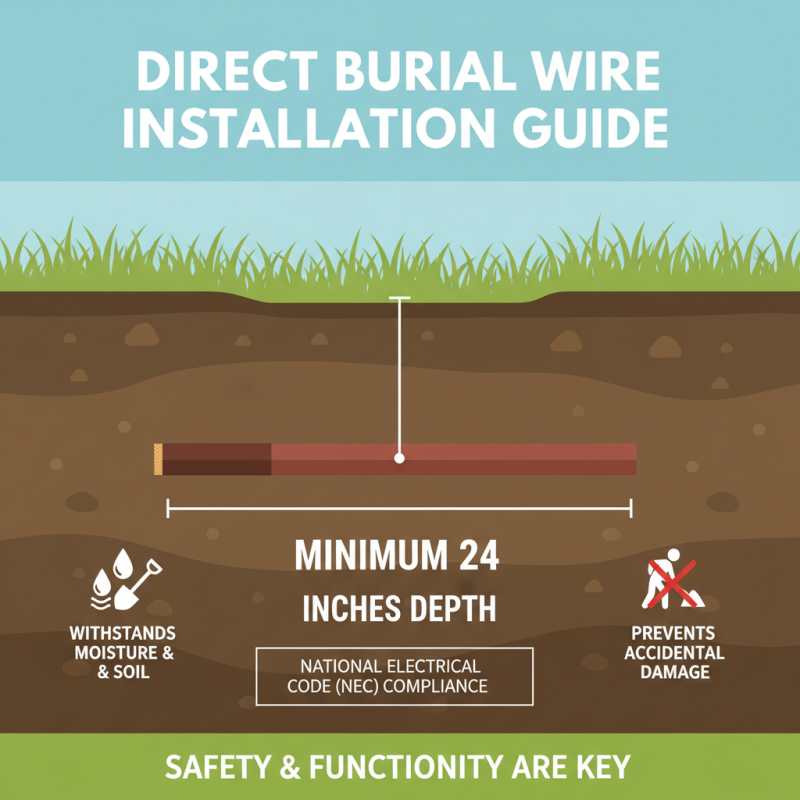
When selecting direct burial wire for electrical projects, adherence to proper installation guidelines is paramount to ensure safety and functionality. Direct burial wire is designed to withstand moisture, soil conditions, and other environmental factors without the need for additional conduit. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), these cables must be rated for direct burial and should typically be laid at a minimum depth of 24 inches to mitigate the risk of accidental damage. This depth is crucial, especially in areas with heavy foot traffic or potential digging activities.
Moreover, the selection of appropriate insulation types, such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLP), is crucial for durability and resistance against moisture. Reports from the U.S. Department of Energy indicate that improper installations can lead to short circuits and electrical hazards, emphasizing the importance of adhering to industry standards. Installing direct burial wire also necessitates consideration of local soil characteristics, which can influence cable performance over time. By understanding the environmental conditions and following installation best practices outlined by industry standards, electricians can significantly reduce the risk of electrical failures and enhance the longevity of their projects.
When selecting direct burial wire for electrical projects, safety should always come first. Direct burial wire is designed for underground installation and is typically used for power distribution, lighting, and other electrical applications. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), proper insulation and protection are critical to prevent moisture ingress and electrical shorts, which can lead to hazards. Installations should follow the NEC guidelines and local regulations to ensure maximum safety.
Before beginning any project, ensure that you assess soil conditions and potential environmental factors. For instance, corrosive soils can affect the longevity of your wiring and increase the risk of shorts. Using wire rated for direct burial, such as THWN or UF, can mitigate issues associated with moisture and temperature fluctuations. In addition, burying the wire at a proper depth, typically at least 24 inches for direct burial, will help avoid accidental damage from surface activities.
Tips: