Choosing the right welding cable for your project can be daunting. Industry expert John Smith, a seasoned welding technician, emphasizes the importance of quality in his statement: "The right welding cable can make or break your project."
Welding cables come in various sizes and materials. Understanding these differences is critical. Selecting the wrong type might lead to inefficiencies or even hazards. Always consider the type of welding you will do. For instance, MIG welding requires different cables than TIG welding.
Moreover, don’t overlook the cable's flexibility. A stiff cable can be challenging to manage in tight spaces. This often leads to mistakes or accidents. Reflecting on past projects can help. Ask yourself what worked and what didn’t. Choosing the correct welding cable involves careful thought and attention. Your project's success may depend on it.

When selecting welding cables, understanding the different types is crucial. There are a few primary categories to consider, like copper and aluminum cables. Copper cables are known for their excellent electrical conductivity. They can carry more current, which is essential for heavy-duty welding tasks. However, they are heavier and pricier than their aluminum counterparts. On the other hand, aluminum cables are lighter and more affordable but may not handle high temperatures as effectively. The choice between them can affect overall efficiency.
Another factor to consider is the cable size. The gauge indicates how much current the cable can safely carry. A smaller gauge means a thicker cable. For instance, a 2-gauge cable is thicker than a 10-gauge one. Using the wrong size can lead to overheating or damage. Many overlook this detail, but it can impact performance significantly. Additionally, remember that cable length also plays a role. Longer cables may lead to voltage drop, affecting welding quality. It's vital to think critically about your project needs before making a decision.
| Cable Type | Wire Gauge | Current Capacity (Amperes) | Application | Insulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Welding Cable | 2 AWG | 175 | MIG and TIG Welding | EPDM |
| H01N2-D Welding Cable | 3 AWG | 150 | Arc Welding | PVC |
| Rubber Welding Cable | 4 AWG | 125 | Stick Welding | Rubber |
| Heavy Duty Welding Cable | 1 AWG | 200 | Heavy Industrial Use | Cross-linked Polyethylene |
Choosing the right welding cable is crucial for a successful project. Consider the cable's ampacity, which is the maximum current it can handle. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), a welding cable must be able to carry the necessary current without overheating. A good rule of thumb suggests that the cable's ampacity should exceed the machine's output by 20%.
When selecting welding cables, also think about their flexibility and insulation type. A rubber-insulated cable offers excellent flexibility, even in cold environments. Reports from industry experts indicate that cables with a lower gauge number are thicker and can carry a higher load. However, they are also heavier and less flexible.
Tips: Always double-check the cable length. Longer cables can lead to voltage drops. This may affect performance. Look for cables that are rated for the specific type of welding you are doing. This ensures safety and efficiency. Don’t overlook the environment where you’ll be working. Outdoor jobs may require more durable cables.
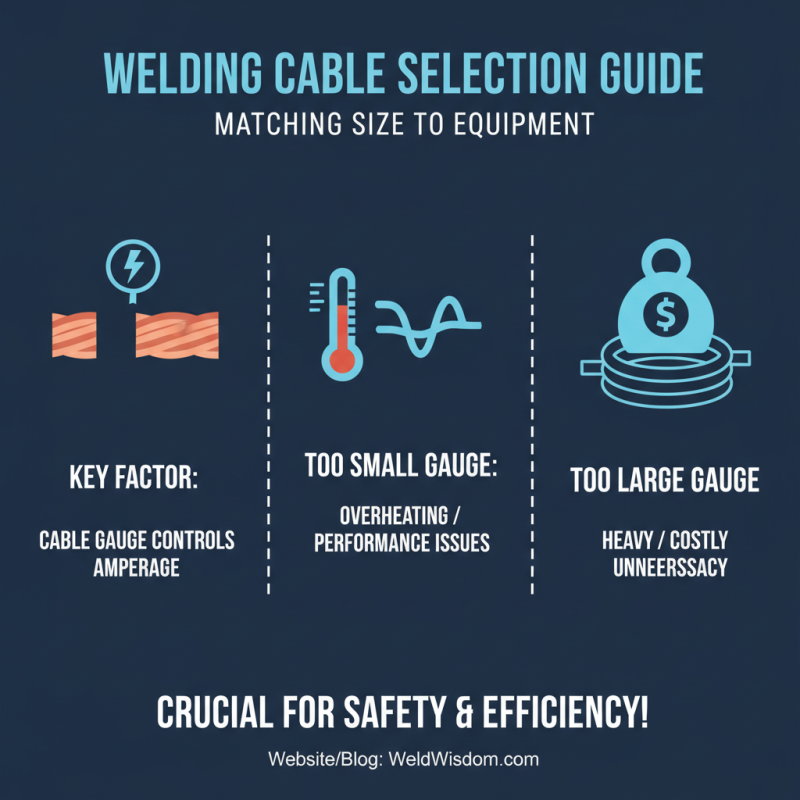
When selecting a welding cable, matching its size to your equipment is crucial. The gauge of the cable is vital. It needs to handle the amperage your welder uses. A smaller gauge can lead to overheating and performance issues. A larger gauge may be unnecessarily heavy and costly.
Check your welding machine's manual for specific requirements. The manual often lists the optimal cable size for best results. For instance, if your welder operates at 200 amps, a lower gauge cable is likely needed. Keep in mind, not all projects are the same. Different tasks require different setups, so flexibility is essential.
Tips: Always calculate the distance from your power source to the work area. Longer distances may require thicker cables to minimize voltage drop. Ensure connections are secure and free of corrosion. Over time, you might notice that even a proper cable can wear out or become damaged, which can affect performance. Regular inspections will help maintain efficiency.
When selecting welding cables, insulation and jacket materials are crucial. These materials directly impact performance and durability. Common insulations include PVC and rubber. PVC is cost-effective but may not withstand extreme heat. Rubber provides better heat resistance but can be more expensive.
Consider the working environment. If moisture or chemicals are present, opt for cables with robust jackets. The jacket protects the inner conductors and prevents damage. Thicker jackets often resist abrasion and cuts. However, they might add weight and reduce flexibility, which can be a hassle on the job.
Reflect on your project needs. Are you working indoors or outdoors? Would you need flexibility or heavy-duty protection? Make a list of conditions to find the right match. Don't overlook the importance of these materials. Choosing poorly can lead to costly mistakes.

When selecting welding cables, safety standards and certifications are crucial factors. Cables must comply with industry benchmarks. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) outlines strict specifications. According to a recent report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), 40% of welding accidents could be prevented by using properly certified cables.
Not all cables meet these safety requirements. For instance, many welding cables lack sufficient insulation. This can lead to dangerous short circuits or electrical shock. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) stresses the need for cables to have adequate ratings. An improperly rated cable increases risks significantly during high-temperature welding tasks.
It’s essential to consider certifications like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and CSA (Canadian Standards Association). These labels indicate that a product has undergone rigorous testing. However, some manufacturers might cut corners to reduce costs. This affects both performance and safety. Inadequate materials can lead to failure under heavy use. Always verify the certification before making a purchase. A minor oversight could lead to major accidents.