In the world of welding and fabrication, the significance of selecting the appropriate welding cable cannot be overstated. As John Smith, a renowned expert in the welding industry, aptly states, "The right welding cable is not just an accessory; it's a lifeline for ensuring safety and efficiency in any welding project." In this context, understanding the intricacies of welding cable selection is crucial for both professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Welding cables are specifically designed to withstand the rigorous demands of welding processes, yet many overlook their critical role in maintaining operational safety and performance standards. Choosing the wrong type of welding cable can lead to increased risks of electrical failures, reduced productivity, and compromised weld quality. Therefore, it is imperative to consider factors such as amperage rating, flexibility, and insulation material when making this essential decision.
As projects vary in scale and complexity, the choice of welding cable can significantly impact the overall execution and outcome. In this article, we will explore why choosing the right welding cable is paramount, examining its implications for workflow efficiency, safety regulations, and the quality of craftsmanship in welding projects.

When it comes to welding applications, choosing the right welding cable is crucial for ensuring both electrical conductivity and safety. According to the American Welding Society, proper cable selection plays a pivotal role in maintaining high levels of current efficiency while also preventing overheating and potential hazards. High-quality welding cables are typically made from oxygen-free copper, which offers superior conductivity compared to standard copper. This ensures that the electrical resistance in the circuit is minimized, maximizing the proficiency of the welding process.
Safety is another critical aspect that hinges on the correct selection of welding cables. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) reports that electrical faults are a leading cause of welding-related incidents and fires. Using cables with inadequate insulation or improper ratings can result in dangerous situations, including electrical shock or fire outbreaks. Cables that meet or exceed industry standards, such as those outlined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), not only enhance operational safety but also contribute to the overall longevity of the welding equipment by reducing the risk of failure. Therefore, investing in the right welding cables is not just a matter of efficiency – it’s also about safeguarding the health and safety of workers and equipment alike.
| Cable Type | Voltage Rating (V) | Current Rating (A) | Conductor Material | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WELDING CABLE 1 | 600 | 200 | Copper | MIG Welding |
| WELDING CABLE 2 | 600 | 250 | Copper | TIG Welding |
| WELDING CABLE 3 | 1000 | 300 | Copper Braid | Stick Welding |
| WELDING CABLE 4 | 600 | 150 | Aluminum | Flux-Core Welding |
| WELDING CABLE 5 | 600 | 400 | Copper | Submerged Arc Welding |
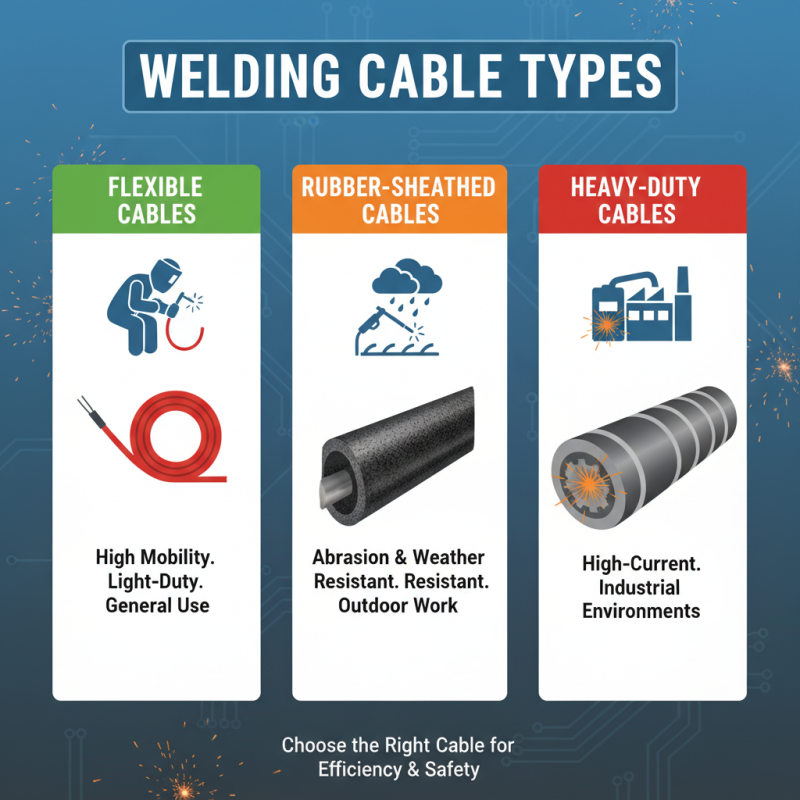
When it comes to welding, the type of welding cable you choose can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of your projects. Understanding the different types of welding cables and their applications is crucial for making the right choice. There are several standard types of welding cables, including flexible cables, rubber-sheathed cables, and heavy-duty cables. Flexible cables are typically used in applications that require high mobility, while rubber-sheathed cables offer excellent resistance to abrasions and environmental conditions, making them ideal for outdoor work. Heavy-duty cables are designed for high-current applications and are well-suited for industrial environments.
Tips: When selecting a welding cable, always consider the specific requirements of your project, such as the type of welding process you'll be using and the environment in which you'll be working. Ensure that the cable’s ampacity matches or exceeds the demands of your welding machine to avoid overheating and potential hazards.
Different environments may require different cables; for instance, if you’re working in wet conditions, it’s advisable to opt for cables with better moisture resistance. Additionally, proper cable maintenance is vital. Regularly inspect your welding cables for any signs of wear or damage and replace them if necessary to ensure safe and reliable operation. By understanding the various types of welding cables and their specific applications, you can choose the right one for your project and enhance your welding experience.
When selecting welding cables for your projects, several key factors must be taken into consideration to ensure optimal performance and safety. First and foremost, the amperage rating of the cable should match or exceed the requirements of the welding equipment being used. This is critical, as using a cable with insufficient amperage may lead to overheating, reduced efficiency, and even safety hazards. Additionally, the cable's insulation material is vital; look for high-quality insulation that can withstand environmental conditions, including moisture, heat, and chemicals, which can significantly affect the cable's longevity and reliability during operation.
Another important aspect to consider is the flexibility and size of the cable. Depending on the nature of your work and the locations where welding will occur, you may need cables that can easily maneuver around obstacles without risking damage or kinks. Thicker cables provide better conductivity, but also tend to be less flexible. Therefore, finding a balance between gauge size and flexibility based on the demands of your particular project is crucial. Lastly, consider the overall length of the cable needed; longer cables may experience voltage drops, so it’s essential to calculate the right length to maintain proper productivity and quality in your welds.

When selecting welding cables, it is crucial to consider the industry standards and regulations that govern their specifications. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) lay down key guidelines for the manufacturing and use of these cables, ensuring safety and efficiency in welding applications. According to the IEEE 837 standard, welding cables must be rated for specific ampacity levels based on their insulation type and environment, which can significantly influence performance and safety during welding operations.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) also provides insights into the necessary resistance levels and thermal properties required for welding cables. For instance, a report by the NFPA highlights that inadequate insulation can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards, emphasizing the need for compliance with the specified voltage rating and temperature range. In addition, the American Welding Society (AWS) outlines the importance of using cables that meet or exceed these guidelines, not only for operational efficiency but also to mitigate risks associated with electrical failures. By adhering to these standards, professionals can ensure a reliable connection and optimal performance for their welding projects.
When it comes to welding, the quality of the welding cable you choose can significantly affect both performance and efficiency. High-quality cables ensure that sufficient current reaches the weld zone, which is vital for achieving strong and durable welds. According to a report from the American Welding Society, using cables that meet the right specifications can enhance arc stability and improve heat distribution, leading to a 15% increase in welding productivity. Poor-quality cables, on the other hand, can introduce resistance and lead to overheating, which may contribute to equipment failure and safety hazards.
Tips: When selecting welding cables, always check the ampacity ratings to ensure they are suitable for your welding application. Cables with greater flexibility allow for easier maneuvering, which is especially important in complex welding projects. Furthermore, consider using cables made with high-quality copper conductors, as they provide better conductivity than aluminum counterparts, reducing energy loss and enhancing overall efficiency.
Moreover, the insulation material of welding cables plays a critical role. Cables equipped with high-temperature and abrasion-resistant insulation can withstand harsh working environments, which is crucial for outdoor and industrial applications. Data from industry analyses indicate that investing in robust insulation can extend the life of welding cables by up to 30% and minimize downtime caused by cable replacement. Make informed choices to ensure optimal performance in your welding projects.