When embarking on electrical projects, one of the most crucial decisions you'll face is selecting the appropriate Single Conductor Wire. This seemingly straightforward choice can significantly impact the performance, safety, and efficiency of your work. Understanding the characteristics and specifications of Single Conductor Wire is essential to ensuring that your project meets its intended objectives while adhering to safety standards.
In this guide, we will explore ten essential tips that will empower you to make informed decisions when choosing Single Conductor Wire. From assessing wire gauge and material to considering environmental factors and electrical requirements, each tip will provide valuable insights that cater to both novice and experienced professionals. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to select the right Single Conductor Wire for your specific needs, enhancing the overall quality and reliability of your electrical projects.
When selecting single conductor wire for various projects, it's crucial to understand the different wire types available. Single conductor wires come in various materials, primarily copper and aluminum, which have distinct benefits. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), copper wires are preferred for their superior conductivity, providing low resistance and better performance across a range of applications—especially in contexts where efficiency is paramount. Alternatively, aluminum wires can offer a lightweight and cost-effective solution, making them suitable for overhead power lines.
Another key aspect to consider is the insulation type and its thermal rating. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) specifies several insulation materials, including PVC, XLPE, and Teflon, each designed to withstand different environmental conditions and heat levels. For instance, PVC insulation is commonly used in residential wiring while XLPE offers higher thermal ratings, making it ideal for industrial applications. Understanding these specifications will not only help in the selection process but also ensure safety and efficacy in your electrical projects, reducing the risk of overheating and potential failures.
When selecting single conductor wire for your projects, understanding wire gauge is crucial. Wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wire, and it directly impacts the wire's capacity to carry current. Using the appropriate gauge is vital to ensure safety and efficiency; a wire that is too thin may overheat and fail, while a wire that is too thick might be unnecessary for your application, leading to increased costs and rigidity.
The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is commonly used to measure wire thickness, where a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire. For most projects, the wire gauge should be matched to the current load it will carry, considering both the length of the wire and the nature of the application. For instance, longer wire runs may require a thicker gauge to account for voltage drop, while the specifics of the project, such as whether it’s for power delivery or signal transmission, can also dictate the best choice. Always evaluate these factors carefully to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your wire installations.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Wire Gauge | Application | Ampacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Determine project requirements | 10 AWG | Power tools | 30 Amps |
| 2 | Consider environmental factors | 12 AWG | Indoor lighting | 20 Amps |
| 3 | Choose appropriate insulation | 14 AWG | Home appliances | 15 Amps |
| 4 | Evaluate length of wire | 16 AWG | Speakers | 10 Amps |
| 5 | Check for flexibility | 18 AWG | Low voltage lighting | 10 Amps |
| 6 | Verify compliance with standards | 20 AWG | Data cables | 3 Amps |
| 7 | Assess the load capacity | 8 AWG | Industrial machinery | 40 Amps |
| 8 | Consider future scalability | 2 AWG | Solar panels | 100 Amps |
| 9 | Factoring in heat dissipation | 4 AWG | Heating cables | 70 Amps |
| 10 | Consult with a professional | 6 AWG | Electrical service | 55 Amps |
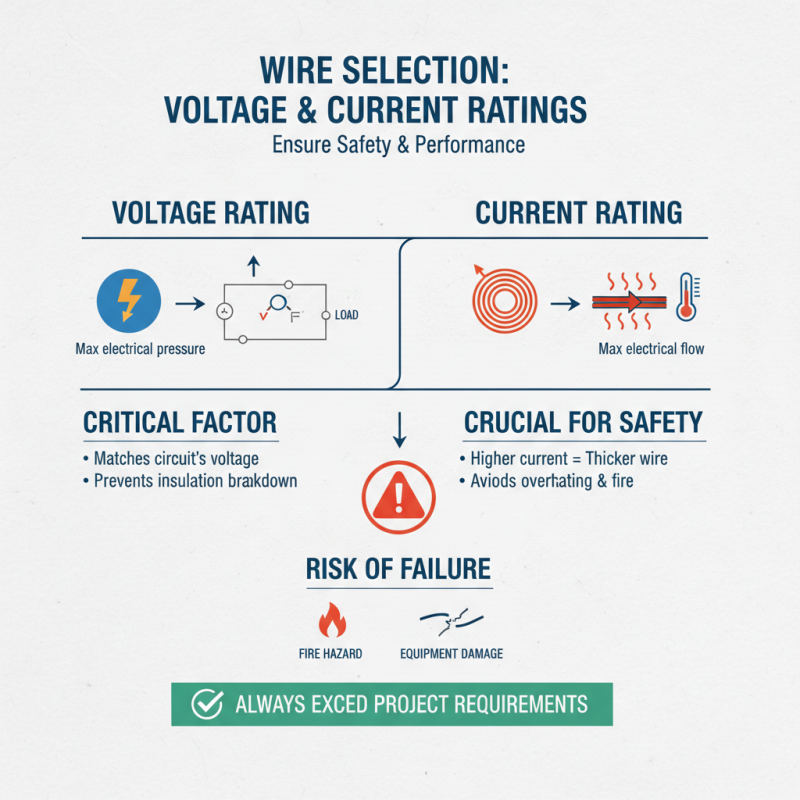
When selecting the right single conductor wire for your projects, one of the most critical factors to consider is its voltage and current ratings. These ratings indicate the maximum voltage and current the wire can safely handle without overheating or failing. Ensuring that your selected wire meets or exceeds the requirements of your application is crucial for optimal performance and safety. For instance, using a wire with an insufficiently rated current capacity can lead to excessive heat buildup, potentially causing insulation failure or even fire hazards.
In addition to matching the voltage and current ratings, it's essential to consider the specific conditions under which the wire will operate. This includes environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or ultraviolet light. Different applications, such as residential wiring or industrial installations, may require wires designed to withstand harsher conditions. By taking the time to assess these parameters carefully, you not only enhance the reliability of your electrical systems but also extend the lifespan of your wire and connected components.
When selecting the right single conductor wire for your projects, one of the most critical factors to consider is the insulation material. The insulation not only protects the conductor from environmental elements but also helps maintain performance in various conditions. Common insulation materials include PVC, XLPE, and rubber, each offering different benefits depending on the environment where the wire will be used.
For outdoor projects, consider using insulation that is UV resistant and can withstand temperature fluctuations. This is particularly important in regions with extreme weather. Moreover, if the wire will be exposed to moisture, selecting an insulation material with waterproof properties is essential to prevent short-circuits and maintain durability. Look for wires that specify their suitability for wet environments to ensure long-term reliability.
When it comes to thermal resistance, materials like silicone rubber can be advantageous in high-temperature applications, allowing the wire to perform efficiently without degradation. Additionally, if your project might involve exposure to chemicals, considering wires with specialized insulation that can resist corrosion and chemical damage is a prudent choice. This attention to insulation material will enhance the longevity and effectiveness of your wiring projects.
When embarking on any electrical project, selecting the right single conductor wire is critical, especially when considering length and cost factors. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), wire costs can vary significantly based on gauge and copper prices, which can be volatile. This means that project budgets must account for current market conditions and potential fluctuations in material costs. Understanding how much wire is needed not only prevents overspending but also ensures efficiency in your project.
To make budget-friendly choices, start by accurately measuring your required wire length, factoring in all installation angles and terminations. Experts advise always adding an extra 10% to your calculated length to account for mistakes or miscalculations. Additionally, be mindful of the wire gauge necessary for your specific load requirements. Using a gauge that is too small can lead to overheating and potential hazards, while selecting a larger gauge than needed can unnecessarily increase costs.
When considering cost, also take into account the long-term savings associated with quality wire. Higher-quality single conductor wire offers better conductivity and is often more durable, leading to fewer replacements and repairs over time. As noted by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), investing in quality materials can ultimately provide a better return on investment, highlighting the importance of balancing initial costs with future performance.






